Vitamin D is needed to rebuild from disease
It appears that certain aspects of medicine are stuck in some time warp—a revolving door that doesn’t stop.
Practitioners use an unreliable and antiquated diagnostic algorithm, an unspecific drop-down menu way of treating people and their ailments.
I’m not talking about the advances in medical science with targeted therapies, gene sequencing, prosthetics, etc, I’m talking about the standard healthcare that is supposed to help people overcome their health issues, prevent recurrence, and just prevent disease in the first place.
Doctors still take blood pressure in only one arm; they run cholesterol testing to determine the perceived risk of heart disease; and they tell patients that their vitamin‑D levels are normal, based on a very old reference range found in routine blood work.
The importance of vitamin D, as well as the need to test vitamin-D levels, is now common knowledge—at least from what I see. Many patients who bring me their blood work have had it tested for various reasons, including chronic health issues and serious disease.
This is great.
The problem is that they have been given false, possibly dangerous, information regarding the proper levels of vitamin D based on their blood work.
Before I tell you the therapeutic levels of vitamin D (not based on a reference range), here’s a quick blurb on how we get vitamin D.
Vitamin D is created when sunlight contacts the skin. It is also ingested though food and, of course, through the use of research-based nutraceuticals (supplements).
Once activated through sunlight or ingested through food, vitamin D travels to the liver then the kidneys, where it becomes a powerful hormone needed for countless reactions and functions in the body.
Some of these functions include:
- Supports the health of the immune system;
- Maintains healthy bones and teeth;
- Regulates insulin levels needed to maintain normal blood sugar;
- Regulates inflammation;
- Controls gene expression involved in the development of cancer;
- Important for heart health and reducing inflammation of the coronary arteries;
- Supports brain function and can reduce depression;
- Boosts weight loss; and
- Responsible for calcium and phosphorous homeostasis.
As you can see, vitamin D plays many roles in the body to stave off disease.
What happens when vitamin D is too low?
Here is a list of health issues found to be linked to low vitamin D:
- Osteoporosis;
- 17 varieties of cancer, including breast, colon, prostate;
- Heart disease;
- High blood pressure;
- Metabolic syndrome;
- Diabetes;
- Obesity;
- Countless autoimmune diseases;
- Gout;
- Infertility;
- PMS;
- Parkinson’s disease;
- Depression;
- Seasonal affective disorder;
- Alzheimer’s disease;
- Chronic fatigue;
- Fibromyalgia;
- Psoriasis; and
- Immune dysfunctions.
If this list is not making an impression, here are some facts regarding vitamin D and cancer. A study published in Annals of Epidemiology found that raising blood levels of vitamin D from 30ng/ml to a higher level of 40 to 60ng/ml would prevent 58,000 new cases of breast cancer (and 49,000 new cases of colorectal cancer) each year.
Although 40ng/ml is still too low, raising it just beyond the standard medical reference range of 30ng/ml had profound effects.
This said, you want your vitamin-D level to be in a specific range in order to prevent chronic and serious health issues. This is known as the therapeutic range.
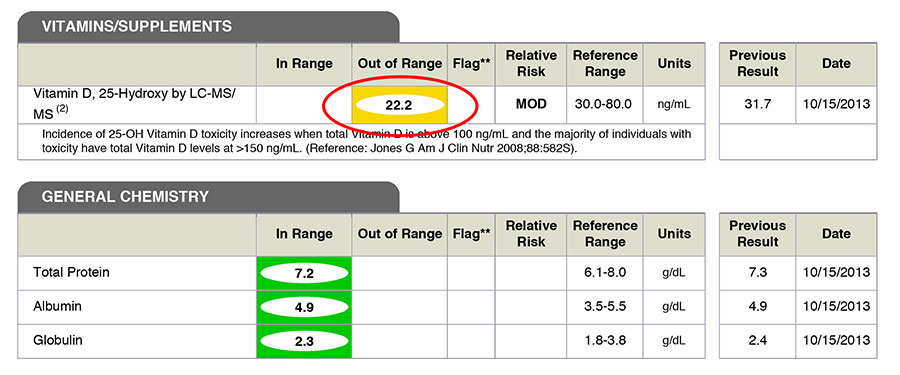
As you look at the levels of vitamin D in your blood work, you will see the lab’s reference range. Typically it is 30-100ng/ml.
However, this is not the therapeutic range needed to prevent disease, or rebuild from one. The therapeutic range you want for vitamin D is closer to 50-80ng/ml.
Most practitioners will simply look to see if your vitamin-D level is within the lab’s reference range and call it a day.
This is irresponsible, as the scientific community is saying that the vitamin-D level needs to be much higher than just 30 or 40ng/ml for good health, and anything below 30ng/ml is dangerous to your health.
Take a look at your blood work and find your vitamin-D3 level. Is it below 30ng/ml?
Is it closer to 50 or even slightly higher than 50ng/ml?
If your vitamin-D level is below 30ng/ml, or even between 30-40ng/ml, you must get those levels up.
How much vitamin D do you need to take to get the level where it needs to be?
Good question.
Because we are all different, it is difficult to give recommendations that will specifically work for you.
However, if your vitamin-D level is low (less than 30ng/ml—40ng/ml), consider taking 4-6000IU/day of a high-end vitamin D3.
Besides supplementing with vitamin D, the foods that provide dietary vitamin D include:
- Fatty fish (Mackerel, Salmon, Sardines);
- Cod liver oil;
- Almond milk; and
- Eggs.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it is best absorbed with fat from the diet. So, take your vitamin-D supplement with your food.
Sunlight Creates Vitamin D
Don’t forget sunlight.
As the dark months are ahead of us, try to get sunlight daily to get the D level up. This doesn’t mean you bake in the sun for hours on end. Rather, let the sunlight hit your skin 30 minutes a day if possible.
Once you start supplementing, getting more sunlight, and eating fatty fish, get your vitamin-D level measured again in 4-6 weeks to see what the new level looks like.
To rebuild from disease, or some chronic health issue, get your vitamin-D level up to 50-80ng.ml.
For more information on rebuilding from disease, go to: www.drzembroski.com/rebuild
Reference
Garland, C. F., Gorham, E. D., Mohr, S. B., & Garland, F. C. (2009). Vitamin D for cancer prevention: Global perspective. Annals of Epidemiology, 19 (7), 468–83.

Hey Dr. Z! It’s been a long time! I am just wondering, as someone who’s vitamin d level is often low, if it’s true that SPF lotion blocks the skin from absorbing the Vitamin D from sunlight? I’ve read that it is ok to go out in the sun for up to 30 minutes without it…would you agree with that? Thanks! This was a very helpful article! Take care, Peggy O.
Hi, nice to hear from you! Yes, SPF lotion does block the the production of vitamin d in the skin. According to The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association, sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher can reduce the body’s vitamin D-3 production by 99 percent. 99%. The reality is, humans need to be in the sun for more than just the production of vitamin D. It’s best to get short exposures to the sun, and 30 minutes at a time is enough without getting sunburn. If the sun doesn’t get your vitamin D level up, start with 4-6000IU a day then redo your blood work. Hope this helps!
I have read that sunblock does box of vitamin D is that true or not
Hi, its my understanding that sunblock blocks UVB radiation from the sun, which is also responsible for creating vitamin D in the skin. If you block UVB radiation, you reduce production of vitamin D
Thanks Dr Z. This is very clear and understandable. A call to action and I will get my blood work updated ASAP.
Good Idea! Remember to eat fatty fish, get some sunlight, and take vitamin D until you get those levels up to 50-90ng/ml in the blood.
Hi Dr. Zembroski. Great post! I love this. It’s informative article. I know that Vitamin D has benefits but I never know that it has a lot of benefits including Heart disease. I heard that Coq 10 Supplements also keep heart health as shown here https://www.eathealthyandthrive.com/best-coq-10-supplements-to-keep-your-heart-healthy/. I wonder if I have to taken both or choose only one. Thank you in advance for your suggestion.
Hi. Both vitamin D and CoQ10 can be taken as part of a nutrient plan for heart health. CoQ10 has been shown to prevent the oxidation of LDL—a major step in the production of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. It is a great anti-oxidant and it provides energy to several major organ systems in the body. Vitamin D has countless benefits one being an anti-inflammatory with evidence that it reduces inflammation found in the atherosclerotic lesions in the arteries. If you are concerned about heart issues and coronary artery disease, its a good idea to take both.
Dr Z very interesting information.Here in Scotland there is a significant link with vit D dificiency in the northern and western isles and MS.
I have a low immune system period as i have had chronic hep b for 35 yrs taking Tenofovir daily and also have to take HRT testosterone as i am Xyy syrd i have partticulary noticed in winter i am more depressed and get sesonal ad ,less energy and i often wondered if this all was connected to lower levels vit D besides the other two issue i have
Anthony, low vitamin D is associated with seasonal affective behavioral issues for sure. Longer hours of darkness can lower brain serotonin levels which also contributes to mood issues and depression when there is less daylight. Everyone needs to get there vitamin D levels higher, and get outdoors during the shorter days. Make sure to get your vitamin D levels up to 60-80ng/ml.
Thanks Dr Zembroski
I found your articles very informative.
I now take a vitmen d spray daily inside my cheek delivering 3000iu and eat raw herrin weekly along with sardines , freash mackeral and eggs also drink almond milk occssionally
My energy levels are much better walking 4 miles plus daily, given up my car, my mood significantly better enthusiastic and sleeping better.i dont feel like a 65 yr old. Full head of hair and muscle tone has improved. Now a great advocate to everyone i meet about increasing vit d levels.
Always been an outdoor person so no probs there.
Also very relavent now having higher levels of the vit d with coviid circulating so all the very best to you for 2021.
WHAT IS the benifits of vitamin d3 for children?
Vitamin D regulates calcium and bone metabolism, controls cell proliferation and differentiation, and exerts immunoregulatory activities. Vitamin D is important for kids and adults the same
Is it beneficial or necessary to take Vitamin K when you take vitamin D?
Nancy, there is some thoughts on taking vitamin K when you supplement with vitamin D. Vitamin D help maintain calcium levels in the blood. Vitamin K helps prevent the deposition of calcium into tissues of the body. However, sunlight creates vitamin D, and not vitamin K in the body. So, is vitamin K necessary? My response would be if you are overdosing on vitamin D—which is insanely rare—vitamin K will help prevent calcium from getting into the tissues including the arteries. I dont take vitamin K with my vitamin D.